Back to article: The long non-coding RNA H19 suppresses carcinogenesis and chemoresistance in hepatocellular carcinoma
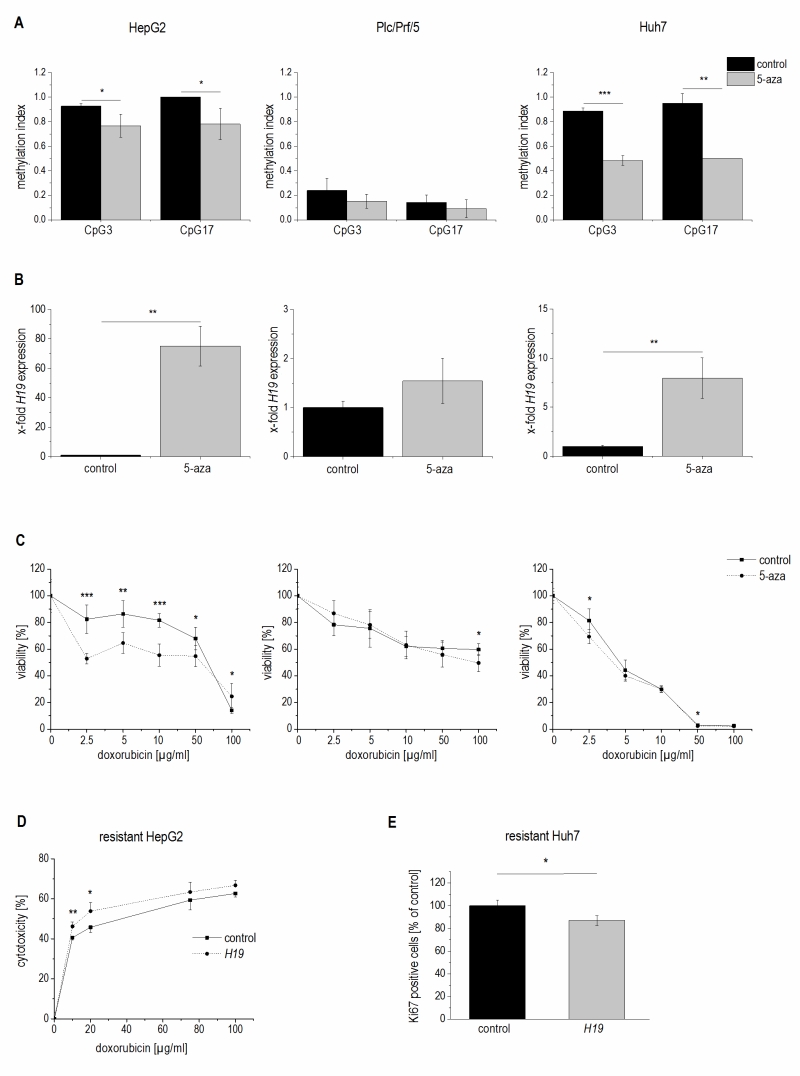
FIGURE 8: Methylation dependent H19 expression and its effect on cell viability and proliferation. (A-C) HepG2 (left panel), Plc/Prf/5 (middle panel), and Huh7 cells (right panel) treated with 5-azacytidine (5-aza) and untreated control cells (control) were analyzed for (A) methylation index of two CpG sites of the H19 promoter by SNuPE (n=2, duplicates), (B) H19 expression determined by qPCR (n=2, duplicates), and (C) viability after treatment with doxorubicin by cytotoxicity assay (n=2, quintuplicates). (D) Cytotoxicity estimated by MTT assay after treatment with doxorubicin in doxorubicin resistant HepG2 either transiently overexpressing H19 (H19) or vector control transfected (control) for 48 h normalized to the respective untreated control (n=2, triplicates). (E) Quantification of Ki67 positive cells by FACS in sorafenib resistant Huh7 either transiently overexpressing H19 (H19) or vector control transfected (control) for 48 h and expressed as percent of control (each, n≥2, duplicates). The p values were calculated by two-sample t-test or Mann-Whitney U test depending on the data distribution. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.