Back to article: Tumor suppressive Ca2+ signaling is driven by IP3 receptor fitness
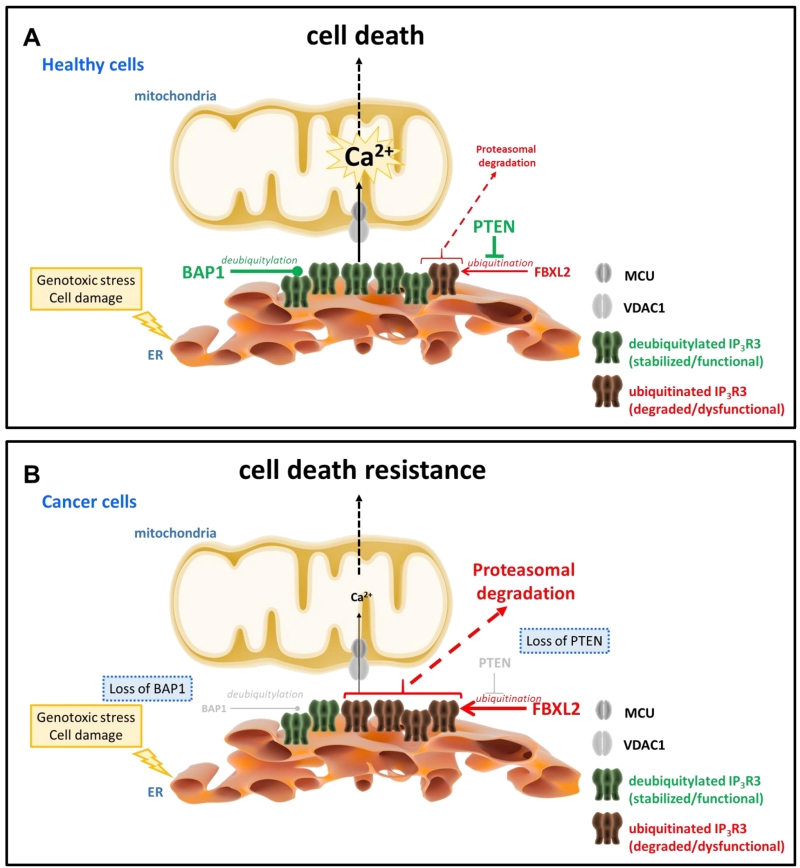
FIGURE 1: IP3R3 channels are targets for ubiquitination and deubiquitylation enzymes, whose activities are deregulated in cancer cells, thereby impacting IP3R3 stability and ultimately cell death sensitivity. (A) IP3Rs, located at the ER-mitochondrial interface, here particularly IP3R3, promote ER-mitochondrial Ca2+ fluxes, thereby enabling adequate cell death sensitivity in healthy cells undergoing genotoxic stress and cell damage, an important feature that prevents oncogenesis. The levels of IP3R3 channels are critical for this process and are dynamically regulated via ubiquitination. BAP1, a tumor suppressor with deubiquitylation enzyme activities and frequently mutated in cancers including mesothelioma, deubiquitylates IP3R3, preventing its proteasomal degradation and resulting in IP3R3 stabilization. In contrast, FBXL2, an F-Box protein with ubiquitin ligase activity, ubiquitinates IP3R3, directing it for proteasomal degradation and resulting in a decline in IP3R3 levels. Importantly, PTEN, another tumor suppressor that antagonizes Akt signaling and frequently mutated in a variety of cancers including prostate cancer, competes with FBXL2 for IP3R3 binding and thus antagonizes FBXL2-mediated ubiquitination of IP3R3, stabilizing IP3R3. In healthy cells, it is anticipated that the balance between deubiquitylation and ubiquitination of IP3R3 channels is favored towards deubiquitylated IP3R3, enabling sufficient IP3R3 channels to sustain adequate ER-mitochondrial Ca2+ fluxes in cells undergoing genotoxic stress and cell damage to engage cell death and eradicate pre-malignant cells with DNA damage. (B) Several cancer types display chromosomal aberrations with defects in the expression of several tumor suppressors, including a reduction in BAP1 levels and a loss in PTEN expression. As a consequence, both alterations will favor IP3R3 ubiquitination and degradation, since reduced BAP1 levels will lead to reduced deubiquitylation of IP3Rs and loss of PTEN will enable FBXL2 to mediate IP3R3 ubiquitination. As a consequence, the balance between ubiquitination and deubiquitylation of IP3R3s will shift towards ubiquitinated IP3R3, impairing ER-mitochondrial Ca2+ fluxes that are needed to engage cell death programs in response to genotoxic stress and cell damage. As such, cells will be able to withstand this cellular stress, resulting in their survival and proliferation despite accumulated DNA damage. This phenomenon is an early event in oncogenesis, enabling malignant cell formation and tumoral behavior.