Back to article: mIDH-associated DNA hypermethylation in acute myeloid leukemia reflects differentiation blockage rather than inhibition of TET-mediated demethylation
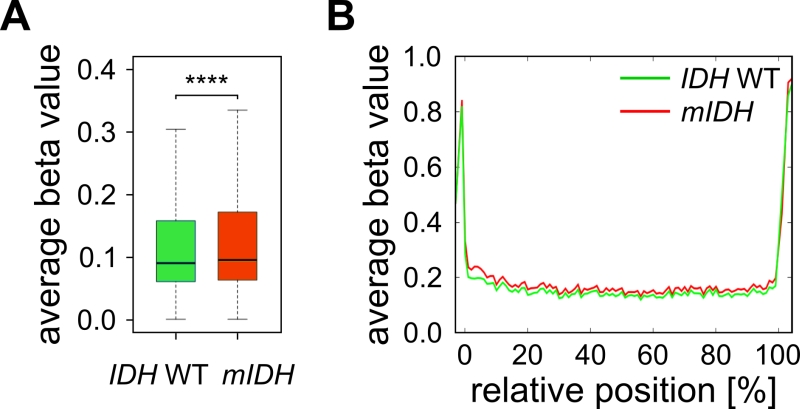
FIGURE 4: TET-dependent DNA methylation canyons are not specifically affected by mIDH-associated hypermethylation in AML. (A) Average methylation ratios of canyon-associated probes in mIDH and IDH WT patients. The difference between the two groups was highly significant (**** P<0.0001). (B) Superposition of all size-normalized canyons depicting average methylation levels of these features in the two patient groups.