Back to article: Putting together and taking apart: assembly and disassembly of the Rad51 nucleoprotein filament in DNA repair and genome stability
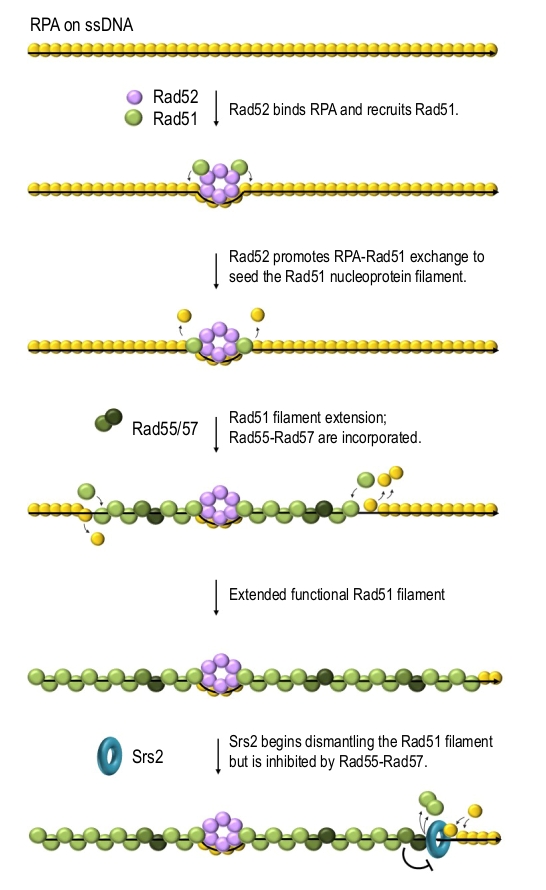
FIGURE 3: A model of Rad51 nucleofilament formation in budding yeast. ssDNA generated as a result of resection or strand separation is rapidly covered by RPA (yellow spheres). Rad52 (purple spheres) binds RPA-coated ssDNA, recruits Rad51 (green spheres) and facilitates RPA-Rad51 exchange in the vicinity, thereby promoting Rad51-ssDNA filament formation. Rad55-Rad57 dimers (dark-green spheres) are also incorporated into the Rad51 nucleofilament and stabilise it by providing additional protein-protein interactions as well as antagonising Rad51 removal by Srs2 (teal ring). Only the main regulators of S. cerevisiae Rad51 are shown.