Back to article: Fine intercellular connections in development: TNTs, cytonemes, or intercellular bridges?
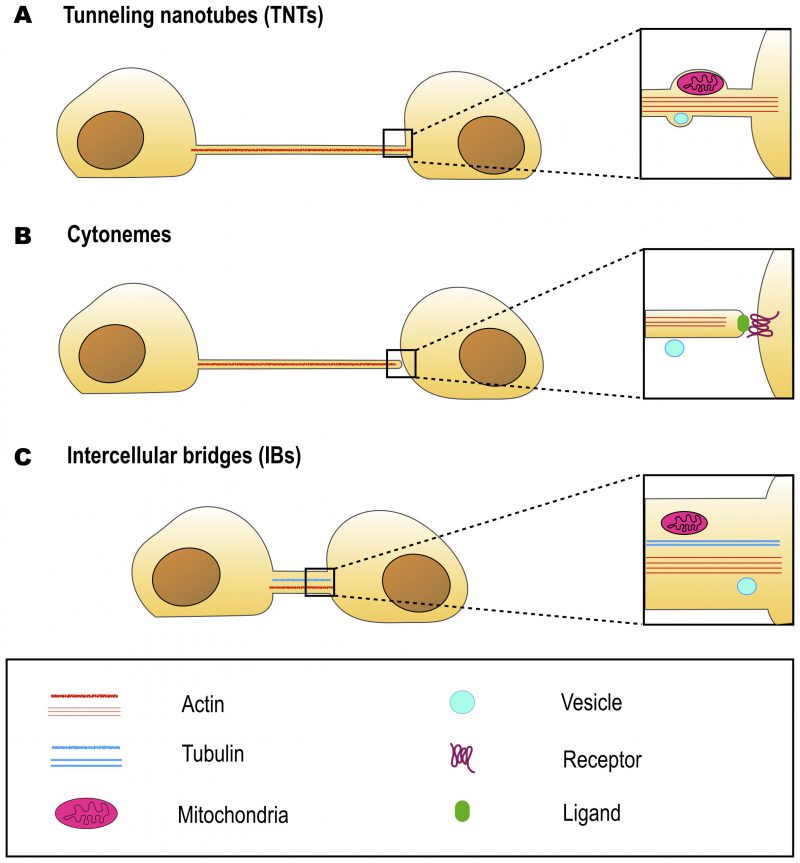
FIGURE 2: Similarities and differences between TNTs, cytonemes and intercellular bridges at optical microscopy level. TNTs (A) and cytonemes (B) have similar morphologies, they contain actin but not tubulin. However, TNTs are open-ended and allow cytoplasm continuity, while cytonemes are closed-ended, and allow protein-protein interactions. Intercellular bridges (C) are open-ended, but are generally shorter and wider than TNTs. Some intercellular bridges were also reported to contain tubulin. All three types of cell structures are able to transfer cargo. However, while cytonemes transfer vesicles on their surface, TNTs and intercellular bridges are able to transfer such organelles as mitochondria in their lumen. As TNT diameter is generally smaller than the diameter of mitochondria, the transfer requires membrane bulging.