Back to article: Ribosome traffic jam in neurodegeneration: decoding hurdles in Huntington disease
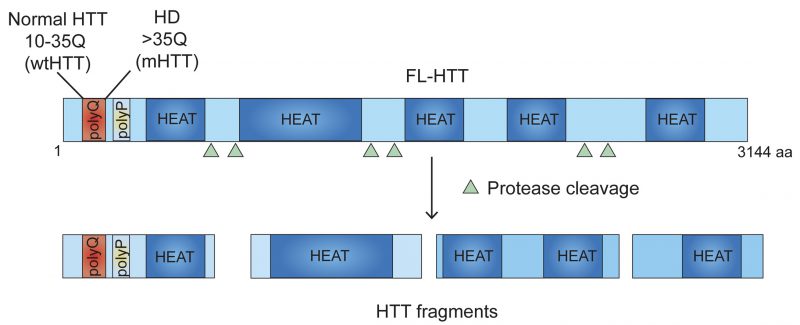
FIGURE 1: Domain structure of HTT protein. HTT consists of 3144 amino acids (aa). PolyQ-polyglutamine tract; polyP-proline-rich domain; HEAT repeats are shown. polyQ and polyP may regulate protein-protein interaction. HEAT repeats may act as scaffolding domain for tethering, localizing, and coordinating the functions of the proteins involved in ribosome elongation, thereby controlling the movement of ribosomes. polyQ expansion in HTT (mHTT) inhibits the movement of ribosomes causing stalling of the polyribosomes. HTT undergoes proteolytic cleavage and generates HTT fragments that may also regulate ribosome movements. Triangle depicts approximate location of protease cleavage sites.