Back to article: How to use a multipurpose SNARE: The emerging role of Snap29 in cellular health
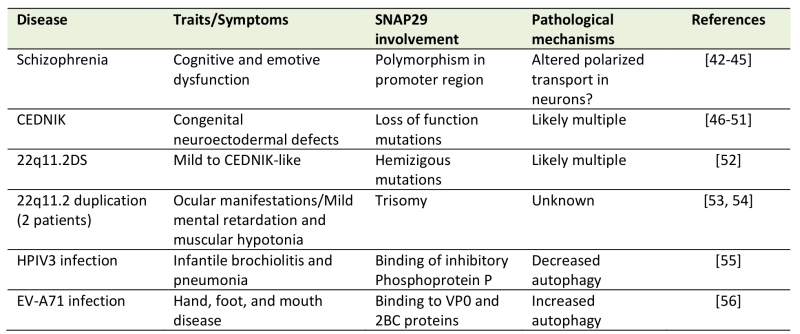
Table 1. List of diseases with proven alterations in SNAP29 (see text for details).
42. Pedrosa E, Shah A, Tenore C, Capogna M, Villa C, Guo X, Zheng D, Lachman HM (2010). beta-catenin promoter ChIP-chip reveals potential schizophrenia and bipolar disorder gene network. J Neurogenet 24(4): 182-193. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/01677063.2010.495182
43. Luo X, Huang L, Han L, Luo Z, Hu F, Tieu R, Gan L (2014). Systematic prioritization and integrative analysis of copy number variations in schizophrenia reveal key schizophrenia susceptibility genes. Schizophr Bull 40(6): 1285-1299. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/schbul/sbu045
44. Frankle WG, Lerma J, Laruelle M (2003). The synaptic hypothesis of schizophrenia. Neuron 39(2): 205-216. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/s0896-6273(03)00423-9
45. Gokhale A, Larimore J, Werner E, So L, Moreno-De-Luca A, Lese-Martin C, Lupashin VV, Smith Y, Faundez V (2012). Quantitative proteomic and genetic analyses of the schizophrenia susceptibility factor dysbindin identify novel roles of the biogenesis of lysosome-related organelles complex 1. Neurosci 32(11): 3697-3711. http://dx.doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.5640-11.2012
46. Sprecher E, Ishida-Yamamoto A, Mizrahi-Koren M, Rapaport D, Goldsher D, Indelman M, Topaz O, Chefetz I, Keren H, O’Brien T J, Bercovich D, Shalev S, Geiger D, Bergman R, Horowitz M, Mandel H (2005). A mutation in SNAP29, coding for a SNARE protein involved in intracellular trafficking, causes a novel neurocutaneous syndrome characterized by cerebral dysgenesis, neuropathy, ichthyosis, and palmoplantar keratoderma. Am J Hum Genet 77(2): 242-251. http://dx.doi.org/10.1086/432556
47. Fuchs-Telem D, Stewart H, Rapaport D, Nousbeck J, Gat A, Gini M, Lugassy Y, Emmert S, Eckl K, Hennies HC, Sarig O, Goldsher D, Meilik B, Ishida-Yamamoto A, Horowitz M, Sprecher E (2011). CEDNIK syndrome results from loss-of-function mutations in SNAP29. Br J Dermatol 164(3): 610-616. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.2010.10133.x
48. Ben-Salem S, Nara S, Al-Shamsi AM, Valle D, Ali BR, Al-Gazali L (2015). New Arab family with cerebral dysgenesis, neuropathy, ichthyosis and keratoderma syndrome suggests a possible founder effect for the c.223delG mutation. J Dermatol 164(3): 610-616. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/1346-8138.12917
49. Diggle CP, Martinez-Garay I, Molnar Z, Brinkworth MH, White E, Fowler E, Hughes R, Hayward BE, Carr IM, Watson CM, Crinnion L, Asipu A, Woodman B, Coletta PL, Markham AF, Dear TN, Bonthron DT, Peckham M, Morrison EE, Sheridan E (2017). A tubulin alpha 8 mouse knockout model indicates a likely role in spermatogenesis but not in brain development. PLoS One 12(4): e0174264. http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0174264
50. Hsu T, Coughlin CC, Monaghan KG, Fiala E, McKinstry RC, Paciorkowski AR, Shinawi M (2017). CEDNIK: Phenotypic and Molecular Characterization of an Additional Patient and Review of the Literature. Child Neurol Open 4: 2329048×17733214. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/2329048×17733214
51. Rapaport D, Lugassy Y, Sprecher E, Horowitz M (2010). Loss of SNAP29 impairs endocytic recycling and cell motility. PloS one 5(3): e9759. http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0009759
52. McDonald-McGinn DM, Fahiminiya S, Revil T, Nowakowska BA, Suhl J, Bailey A, Mlynarski E, Lynch DR, Yan AC, Bilaniuk LT, Sullivan KE, Warren ST, Emanuel BS, Vermeesch JR, Zackai EH, Jerome-Majewska LA (2013). Hemizygous mutations in SNAP29 unmask autosomal recessive conditions and contribute to atypical findings in patients with 22q11.2DS. J Med Genet 50(2): 80-90. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/jmedgenet-2012-101320
53. Cordovez JA, Capasso J, Lingao MD, Sadagopan KA, Spaeth GL, Wasserman BN, Levin AV (2014). Ocular manifestations of 22q11.2 microduplication. Ophthalmology 121(1): 392-398. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2013.06.040
54. Pebrel-Richard C, Kemeny S, Gouas L, Eymard-Pierre E, Blanc N, Francannet C, Tchirkov A, Goumy C, Vago P (2012). An atypical 0.8 Mb inherited duplication of 22q11.2 associated with psychomotor impairment. Eur Journal Med Genet 55(11): 650-655. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmg.2012.06.014
55. Ding B, Zhang G, Yang X, Zhang S, Chen L, Yan Q, Xu M, Banerjee AK, Chen M (2014). Phosphoprotein of human parainfluenza virus type 3 blocks autophagosome-lysosome fusion to increase virus production. Cell Host Microbe 15(5): 564-577. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2014.04.004
56. Lai JKF, Sam IC, Verlhac P, Baguet J, Eskelinen EL, Faure M, Chan YF (2017). 2BC Non-Structural Protein of Enterovirus A71 Interacts with SNARE Proteins to Trigger Autolysosome Formation. Viruses 9(7). http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/v9070169