Back to article: Fatty acids - from energy substrates to key regulators of cell survival, proliferation and effector function
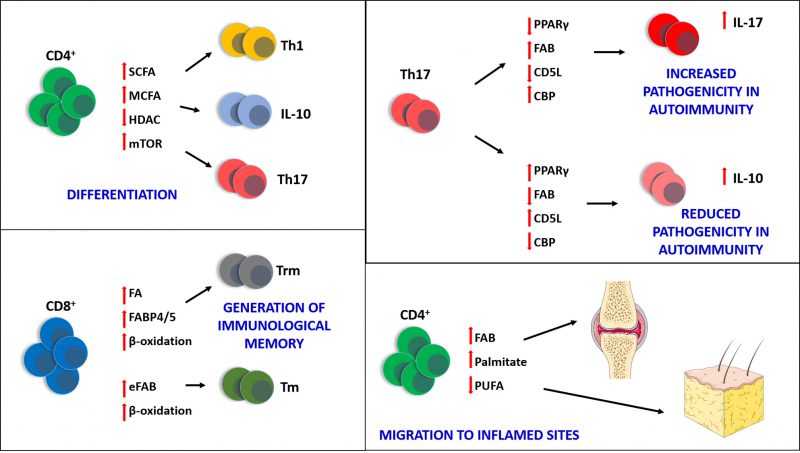
FIGURE 1: Fatty acids are crucial to many biological processes occurring in immune cells, particularly T lymphocytes. Short (C2-4)- and medium (C6-14) chain fatty acids (SCFA and MCFA) are able to influence the differentiation of CD4+ in Th1, Th17 and IL-10+ T cells, by downregulating histone deacetylase (HDAC) activity and activating mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR). The generation of CD8+ tissue resident memory T cells (Trm) also relies upon the availability of fatty acids (FA) available for β-oxidation and the presence of the fatty acid binding proteins FABP4 and FABP5. The generation of central memory CD8+ T cells (Tm) instead relies upon endogenous fatty acid biosynthesis (eFAB), which also provides substrates for β-oxidation, crucial for the long-term survival of these cells. The pathogenicity of Th17 can be also regulated by fatty acids: by increasing the activity of fatty acid biosynthesis (FAB) and cholesterol biosynthesis (CBP), and downregulating the expression of PPARγ and CD5L, Th17 cells produce IL17 and become more pathogenic, especially in auto-immune diseases such as multiple sclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis. Conversely, upregulation of PPARγ and CD5L, and blocking of FAB and CBP, can reduce the pathogenicity of Th17 and increase production of IL10. Finally, saturated fatty acids (e.g. palmitate) can enable the migration of T cells towards non-lymphoid inflamed sites (e.g. joints in arthritis and fat tissue in obesity) where they sustain chronic inflammation; polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) can have the opposite effect and inhibit T cell migration, exerting anti-inflammatory properties.