Back to article: Metabolism remodeling in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
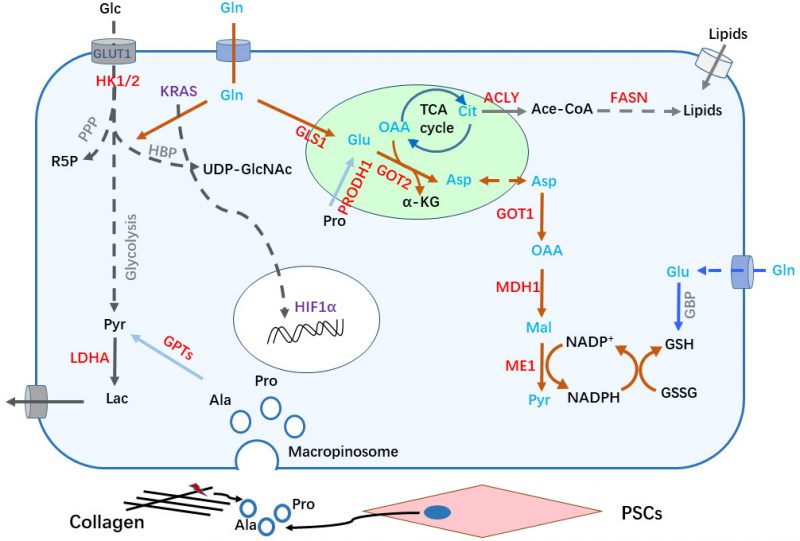
FIGURE 2: Metabolic remolding in PDAC cells. (1) KRAS (in cytoplasm) and HIF1α activation in PDAC cells upregulates glucose transporter (GLUT1) and other glycolytic related genes to promote glucose (Glc) uptake and enhance glycolysis flux, including the production of lactate (Lac) and carbon donation into the hexosamine biosynthetic pathway (HBP) and pentose phosphate pathway (PPP). (2) KRAS activation reprograms Gln metabolism to balance cellular redox homeostasis. Gln is sequentially converted to Glu and Asp catalyzed by GLS1 and GOT2 in the mitochondria, Asp is shuttled to the cytoplasm and generates NADPH after a series of reactions to maintain redox homeostasis. (3) The lipid synthesis pathway is activated, citrate is shuttled from the mitochondria into the cytoplasm to produce acetyl CoA (Ace-CoA), thereby enhancing de novo lipid synthesis pathway. Concomitantly, uptake of exogenous lipids is increased to meet the demand of nutrients for rapid proliferation. (4) The tumor microenvironment, including ECM components and stromal cells, also provide various metabolites/nutrients for PDAC cells, such as Ala and Pro derived from collagen degradation or pancreatic stellate cells (PSCs) secretion. The gene expression of molecules labeled in red color are up-regulated. α-KG: alpha ketoglutarate; Ace-CoA: acetyl-Coenzyme A; ACLY: ATP-citrate lyase; Ala: alanine; Asp: aspartate; Cit: citrate; FASN: fatty acid synthase; Glc: glucose; Gln: glutamine; GLS1: glutaminase; Glu: glutamate; GOT: glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase; GPT: glutamic pyruvic transaminase; GSH: glutathione reduced; GSSG: glutathione oxidized; HBP: hexamine biosynthetic pathway; HIF: hypoxia-inducible factor; Lac: lactate; LDHA: lactate dehydrogenase A; MDH: malate dehydrogenase; ME: malic enzyme; OAA: oxaloacetic acid; PPP: pentose phosphate pathway; Pro: proline; PRODH1: proline dehydrogenase; PSC: pancreatic stellate cell; Pyr: pyruvate; R5P: ribose-5-phosphate; TCA: tricarboxylic acid.